ICT is an acronym that stands for Information Communications Tecnology
However, apart from explaining an acronym, there is not a universally accepted defininition of ICT? Why? Because the concepts, methods and applications involved in ICT are constantly evolving on an almost daily basis. Its difficult to keep up with the changes - they happen so fast.
Lets focus on the three words behind ICT:
- INFORMATION
- COMMUNICATIONS
- TECHNOLOGY
A good way to think about ICT is to consider all the uses of digital technology that already exist to help individuals, businesses and organisations use information.
ICT covers any product that will store, retrieve, manipulate, transmit or receive information electronically in a digital form. For example, personal computers, digital television, email, robots.
So ICT is concerned with the storage, retrieval, manipulation, transmission or receipt of digital data. Importantly, it is also concerned with the way these different uses can work with each other.
In business, ICT is often categorised into two broad types of product: -
(1) The traditional computer-based technologies (things you can typically do on a personal computer or using computers at home or at work); and
(2) The more recent, and fast-growing range of digital communication technologies (which allow people and organisations to communicate and share information digitally)
Let's take a brief look at these two categories to demonstrate the kinds of products and ideas that are covered by ICT:
Traditional Computer Based Technologies
These types of ICT include:
Application Use
Standard Office Applications - Main Examples
Word processing
E.g. Microsoft Word: Write letters, reports etc
Spreadsheets
E.g. Microsoft Excel; Analyse financial information; calculations; create forecasting models etc
Database software
E.g. Oracle, Microsoft SQL Server, Access; Managing data in many forms, from basic lists (e.g. customer contacts through to complex material (e.g. catalogue)
Presentation software
E.g. Microsoft PowerPoint; make presentations, either directly using a computer screen or data projector. Publish in digital format via email or over the Internet
Desktop publishing
E.g. Adobe Indesign, Quark Express, Microsoft Publisher; produce newsletters, magazines and other complex documents.
Graphics software
E.g Adobe Photoshop and Illustrator; Macromedia Freehand and Fireworks; create and edit images such as logos, drawings or pictures for use in DTP, web sites or other publications
Specialist Applications - Examples (there are many!)
Accounting package
E.g. Sage, Oracle; Manage an organisation's accounts including revenues/sales, purchases, bank accounts etc. A wide range of systems is available ranging from basic packages suitable for small businesses through to sophisticated ones aimed at multinational companies.
Computer Aided Design Computer Aided Design (CAD) is the use of computers to assist the design process. Specialised CAD programs exist for many types of design: architectural, engineering, electronics, roadways
Customer Relations Management (CRM)
Software that allows businesses to better understand their customers by collecting and analysing data on them such as their product preferences, buying habits etc. Often linked to software applications that run call centres and loyalty cards for example.
Traditional Computer Based Technologies
The C part of ICT refers to the communication of data by electronic means, usually over some distance. This is often achieved via networks of sending and receiving equipment, wires and satellite links.
The technologies involved in communication tend to be complex. You certainly don't need to understand them for your ICT course. However, there are aspects of digital communications that you needs to be aware of. These relate primarily to the types of network and the ways of connecting to the Internet. Let's look at these two briefly (further revision notes provide much more detail to support your study).
Internal networks
Usually referred to as a local area network (LAN), this involves linking a number of hardware items (input and output devices plus computer processing) together within an office or building.
The aim of a LAN is to be able to share hardware facilities such as printers or scanners, software applications and data. This type of network is invaluable in the office environment where colleagues need to have access to common data or programmes.
External networks
Often you need to communicate with someone outside your internal network, in this case you will need to be part of a Wide Area Network (WAN). The Internet is the ultimate WAN - it is a vast network of networks.
ICT in a Broader Context
Your ICT course will almost certainly cover the above examples of ICT in action, perhaps focusing on the use of key applications such as spreadsheets, databases, presentation, graphics and web design software.
It will also consider the following important topics that deal with the way ICT is used and managed in an organisation:
- The nature of information (the "I" in ICT); this covers topics such as the meaning and value of information; how information is controlled; the limitations of ICT; legal considerations
- Management of information - this covers how data is captured, verified and stored for effective use; the manipulation, processing and distribution of information; keeping information secure; designing networks to share information
- Information systems strategy - this considers how ICT can be used within a business or organisation as part of achieving goals and objectives
As you can see, ICT is a broad and fast-changing subject. We hope our free study materials (revision notes, quizzes, presentations etc) will help you master IT!
Tuesday, November 2, 2010
Monday, June 21, 2010
COMPUTERRISED AND NON-COMPUTERISED SYSTEMS
COMPUTER SYSTEM
A system is an arrangement of elements that when it is put together it becomes an organised and established procedure. A system typically consists of components connected together in order to facilitate the flow of information, matter or energy.
A computer system consists of a set of hardware and software which processes data in a meaningful way.
EDUCATION
• education is the science of teaching and learning of specific skills
• it also imparts knowledge, good judgement and wisdom
BANKING SYSTEM
BANKING BEFORE ICT
• banking was done manually by taking deposits directly
• transactions can only be made during working hours
• takes time to approve any loan applications
BANKING WITH ICT
• all transactions are done by computers
• transaction can be done at anytime and place
• online services, phone banking system, credit cards are available
INDUSTRY
INDUSTRY BEFORE ICT
Production was slow because everything was done manually and totally depended on human labour.
INDUSTRY WITH ICT
Computers and telecommunications industry became very opular and profitable since production can be increased through an all day operation.
COMMERCE
Commerce is an activity of exchanging, buying and selling of commodities on a large scale involving transportation from place to place.
COMMERCE BEFORE ICT
• Trading was made using the barter system and it was then later developed
into currency.
• Advertisement was in the form of word of mouth, billboards and printed
flyers.
• Trading globally was extremely slow, late and expensive. Traders had to find
ways to market local products in the global market.
COMMERCE WITH ICT
E-commerce plays an important role in the economic scene. It includes distribution, buying, selling and servicing products that are done electronically.
A system is an arrangement of elements that when it is put together it becomes an organised and established procedure. A system typically consists of components connected together in order to facilitate the flow of information, matter or energy.
A computer system consists of a set of hardware and software which processes data in a meaningful way.
EDUCATION
• education is the science of teaching and learning of specific skills
• it also imparts knowledge, good judgement and wisdom
BANKING SYSTEM
BANKING BEFORE ICT
• banking was done manually by taking deposits directly
• transactions can only be made during working hours
• takes time to approve any loan applications
BANKING WITH ICT
• all transactions are done by computers
• transaction can be done at anytime and place
• online services, phone banking system, credit cards are available
INDUSTRY
INDUSTRY BEFORE ICT
Production was slow because everything was done manually and totally depended on human labour.
INDUSTRY WITH ICT
Computers and telecommunications industry became very opular and profitable since production can be increased through an all day operation.
COMMERCE
Commerce is an activity of exchanging, buying and selling of commodities on a large scale involving transportation from place to place.
COMMERCE BEFORE ICT
• Trading was made using the barter system and it was then later developed
into currency.
• Advertisement was in the form of word of mouth, billboards and printed
flyers.
• Trading globally was extremely slow, late and expensive. Traders had to find
ways to market local products in the global market.
COMMERCE WITH ICT
E-commerce plays an important role in the economic scene. It includes distribution, buying, selling and servicing products that are done electronically.
Monday, May 10, 2010
A software development process is a structure imposed on the development of a software product. Similar terms include software life cycle and software process. There are several models for such processes, each describing approaches to a variety of tasks or activities that take place during the process. Some people consider a lifecycle model a more general term and a software development process a more specific term. For example, there are many specific software development processes that 'fit' the spiral lifecycle model.
Overview:
The large and growing body of software development organizations implement process methodologies. Many of them are in the defense industry, which in the U.S. requires a rating based on 'process models' to obtain contracts.
The international standard for describing the method of selecting, implementing and monitoring the life cycle for software is ISO 12207.
A decades-long goal has been to find repeatable, predictable processes that improve productivity and quality. Some try to systematize or formalize the seemingly unruly task of writing software. Others apply project management techniques to writing software. Without project management, software projects can easily be delivered late or over budget. With large numbers of software projects not meeting their expectations in terms of functionality, cost, or delivery schedule, effective project management appears to be lacking.
Organizations may create a Software Engineering Process Group (SEPG), which is the focal point for process improvement. Composed of line practitioners who have varied skills, the group is at the center of the collaborative effort of everyone in the organization who is involved with software engineering process improvement.
..Software development activities..
Planning:
The important task in creating a software product is extracting the requirements or requirements analysis.Customers typically have an abstract idea of what they want as an end result, but not what software should do. Incomplete, ambiguous, or even contradictory requirements are recognized by skilled and experienced software engineers at this point. Frequently demonstrating live code may help reduce the risk that the requirements are incorrect.
Once the general requirements are gathered from the client, an analysis of the scope of the development should be determined and clearly stated. This is often called a scope document.
Certain functionality may be out of scope of the project as a function of cost or as a result of unclear requirements at the start of development. If the development is done externally, this document can be considered a legal document so that if there are ever disputes, any ambiguity of what was promised to the client can be clarified.
Implementation, testing and documenting:
Implementation is the part of the process where software engineers actually program the code for the project.
Software testing is an integral and important part of the software development process. This part of the process ensures that defects are recognized as early as possible.
Documenting the internal design of software for the purpose of future maintenance and enhancement is done throughout development. This may also include the writing of an API, be it external or internal. its verty important to document everything in the project
Deployment and maintenance:
Deployment starts after the code is appropriately tested, is approved for release and sold or otherwise distributed into a production environment.
Software Training and Support is important and a lot of developers fail to realize that. It would not matter how much time and planning a development team puts into creating software if nobody in an organization ends up using it. People are often resistant to change and avoid venturing into an unfamiliar area, so as a part of the deployment phase, it is very important to have training classes for new clients of your software.
Maintaining and enhancing software to cope with newly discovered problems or new requirements can take far more time than the initial development of the software. It may be necessary to add code that does not fit the original design to correct an unforeseen problem or it may be that a customer is requesting more functionality and code can be added to accommodate their requests. If the labor cost of the maintenance phase exceeds 25% of the prior-phases' labor cost, then it is likely that the overall quality of at least one prior phase is poor. In that case, management should consider the option of rebuilding the system (or portions) before maintenance cost is out of control.
Bug Tracking System tools are often deployed at this stage of the process to allow development teams to interface with customer/field teams testing the software to identify any real or perceived issues. These software tools, both open source and commercially licensed, provide a customizable process to acquire, review, acknowledge, and respond to reported issues.
Programming Language Approdcues
Electronic commerce with its use of programmable smart cards and payment via Internet must guarantee the confidentiality and integrity of the data involved in the transactions. The ever-increasing presence of software in these applications means that verifying that this software conforms to such security requirements becomes an all-important task which is far from trivial. The Lande research team at IRISA (Inria-Rennes) studies formal techniques for verifying security properties of applications written in the Java programming language and its dialect Java Card, destined for smart card programming.
A number of programming languages incorporate facilities for rendering a program secure eg, by protecting data from unwanted access or by limiting the capabilities of parts of code whose behaviour cannot be trusted. Using a high-level language to express the security management in a program (as opposed to relying on low-level or hardware mechanisms) facilitates formal reasoning about its correctness and opens up the possibility of using well-established techniques from programming language semantics to structure this reasoning. A recent example is Java that comes equipped with a complex security architecture which includes visibility modifiers to limit the accessibility of members of classes, the use of class loaders to create separate name spaces, granting of user-defined permissions such as reading and writing files, and dynamic checks that the executing code has a given permission.
The aim of our research is to develop methods that allow to verify security claims of such applications in a formal manner. This involves two activities: the formalisation of what a security claim is and a semantic model of the Java security architecture against which these security claims can be checked. Our initial effort has focussed on control-flow-based security that for a given code traces back in the execution history to discover on whose behalf it is executing, in order to check that those who originated the current operation indeed have the right to do so. Prior to verification, a program is submitted to a type analysis that for each (virtual) method invocation in the program returns an approximation of the set of concrete methods to which this invocation can correspond - this results in an approximate control flow graph for the program. From this graph we derive a transition system where the states are call stacks and where transitions are method invocations. The security properties to verify are formalised using a temporal logic that describes the allowed paths that can be taken in this transition system. The transition system is infinite and we rely on a novel reduction technique that for a given property allows to restrict attention to a finite part of the transition system in order to verify the validity of the property. The actual verification then becomes a classical model-checking problem.
Ongoing research in the group aims at extending these results in two directions. First, the current method requires that all of the program to verify must be present. This is a limitation in a world where code is loaded dynamically over networks. In order to solve this problem we are looking at how to modularise the various static analyses involved. The aim is a technique that for each unknown piece of code derives a security interface, ie, a security property that an imported piece of code must satisfy in order to be loaded. Second, we are in the process of applying this technique to the Java Card language for programming smart cards. Java Card is derived from Java by removing a number of language features that are too costly and not strictly necessary to implement on the resource-limited smart cards (no multi-threading, no floating-point values, no dynamic class loading etc.). The security model is somewhat different in that applications are completely isolated and communicate via explicitly shared objects. This activity is conducted in collaboration with Bull via the GIE Dyade between INRIA and Bull, and in the INRIA-sponsored research action Java Card, co-ordinated by the Lande research team.
Electronic commerce with its use of programmable smart cards and payment via Internet must guarantee the confidentiality and integrity of the data involved in the transactions. The ever-increasing presence of software in these applications means that verifying that this software conforms to such security requirements becomes an all-important task which is far from trivial. The Lande research team at IRISA (Inria-Rennes) studies formal techniques for verifying security properties of applications written in the Java programming language and its dialect Java Card, destined for smart card programming.
A number of programming languages incorporate facilities for rendering a program secure eg, by protecting data from unwanted access or by limiting the capabilities of parts of code whose behaviour cannot be trusted. Using a high-level language to express the security management in a program (as opposed to relying on low-level or hardware mechanisms) facilitates formal reasoning about its correctness and opens up the possibility of using well-established techniques from programming language semantics to structure this reasoning. A recent example is Java that comes equipped with a complex security architecture which includes visibility modifiers to limit the accessibility of members of classes, the use of class loaders to create separate name spaces, granting of user-defined permissions such as reading and writing files, and dynamic checks that the executing code has a given permission.
The aim of our research is to develop methods that allow to verify security claims of such applications in a formal manner. This involves two activities: the formalisation of what a security claim is and a semantic model of the Java security architecture against which these security claims can be checked. Our initial effort has focussed on control-flow-based security that for a given code traces back in the execution history to discover on whose behalf it is executing, in order to check that those who originated the current operation indeed have the right to do so. Prior to verification, a program is submitted to a type analysis that for each (virtual) method invocation in the program returns an approximation of the set of concrete methods to which this invocation can correspond - this results in an approximate control flow graph for the program. From this graph we derive a transition system where the states are call stacks and where transitions are method invocations. The security properties to verify are formalised using a temporal logic that describes the allowed paths that can be taken in this transition system. The transition system is infinite and we rely on a novel reduction technique that for a given property allows to restrict attention to a finite part of the transition system in order to verify the validity of the property. The actual verification then becomes a classical model-checking problem.
Ongoing research in the group aims at extending these results in two directions. First, the current method requires that all of the program to verify must be present. This is a limitation in a world where code is loaded dynamically over networks. In order to solve this problem we are looking at how to modularise the various static analyses involved. The aim is a technique that for each unknown piece of code derives a security interface, ie, a security property that an imported piece of code must satisfy in order to be loaded. Second, we are in the process of applying this technique to the Java Card language for programming smart cards. Java Card is derived from Java by removing a number of language features that are too costly and not strictly necessary to implement on the resource-limited smart cards (no multi-threading, no floating-point values, no dynamic class loading etc.). The security model is somewhat different in that applications are completely isolated and communicate via explicitly shared objects. This activity is conducted in collaboration with Bull via the GIE Dyade between INRIA and Bull, and in the INRIA-sponsored research action Java Card, co-ordinated by the Lande research team.
Thursday, April 22, 2010
Programming language
A programming language is an artificial language designed to express computations that can be performed by a machine, particularly a computer. Programming languages can be used to create programs that control the behavior of a machine, to express algorithms precisely, or as a mode of human communication.
Many programming languages have some form of written specification of their syntax (form) and semantics (meaning). Some languages are defined by a specification document. For example, the C programming language is specified by an ISO Standard. Other languages, such as Perl, have a dominant implementation that is used as a reference.
The earliest programming languages predate the invention of the computer, and were used to direct the behavior of machines such as Jacquard looms and player pianos. Thousands of different programming languages have been created, mainly in the computer field, with many more being created every year. Most programming languages describe computation in an imperative style, i.e., as a sequence of commands, although some languages, such as those that support functional programming or logic programming, use alternative forms of description.
Definitions-
A programming language is a notation for writing programs, which are specifications of a computation or algorithm.[1] Some, but not all, authors restrict the term "programming language" to those languages that can express all possible algorithms.[1][2] Traits often considered important for what constitutes a programming language include:
Function and target: A computer programming language is a language[3] used to write computer programs, which involve a computer performing some kind of computation[4] or algorithm and possibly control external devices such as printers, disk drives, robots,[5] and so on. For example PostScript programs are frequently created by another program to control a computer printer or display. More generally, a programming language may describe computation on some, possibly abstract, machine. It is generally accepted that a complete specification for a programming language includes a description, possibly idealized, of a machine or processor for that language.[6] In most practical contexts, a programming language involves a computer; consequently programming languages are usually defined and studied this way.[7] Programming languages differ from natural languages in that natural languages are only used for interaction between people, while programming languages also allow humans to communicate instructions to machines.
Abstractions: Programming languages usually contain abstractions for defining and manipulating data structures or controlling the flow of execution. The practical necessity that a programming language support adequate abstractions is expressed by the abstraction principle;[8] this principle is sometimes formulated as recommendation to the programmer to make proper use of such abstractions.[9]
Expressive power: The theory of computation classifies languages by the computations they are capable of expressing. All Turing complete languages can implement the same set of algorithms. ANSI/ISO SQL and Charity are examples of languages that are not Turing complete, yet often called programming languages.[10][11]
Markup languages like XML, HTML or troff, which define structured data, are not generally considered programming languages.[12][13][14] Programming languages may, however, share the syntax with markup languages if a computational semantics is defined. XSLT, for example, is a Turing complete XML dialect.[15][16][17] Moreover, LaTeX, which is mostly used for structuring documents, also contains a Turing complete subset.[18][19]
The term computer language is sometimes used interchangeably with programming language.[20] However, the usage of both terms varies among authors, including the exact scope of each. One usage describes programming languages as a subset of computer languages.[21] In this vein, languages used in computing that have a different goal than expressing computer programs are generically designated computer languages. For instance, markup languages are sometimes referred to as computer languages to emphasize that they are not meant to be used for programming.[22] Another usage regards programming languages as theoretical constructs for programming abstract machines, and computer languages as the subset thereof that runs on physical computers, which have finite hardware resources.[23] John C. Reynolds emphasizes that formal specification languages are just as much programming languages as are the languages intended for execution. He also argues that textual and even graphical input formats that affect the behavior of a computer are programming languages, despite the fact they are commonly not Turing-complete, and remarks that ignorance of programming language concepts is the reason for many flaws in input formats.
Elements-
All programming languages have some primitive building blocks for the description of data and the processes or transformations applied to them (like the addition of two numbers or the selection of an item from a collection). These primitives are defined by syntactic and semantic rules which describe their structure and meaning respectively.
Syntax-
A programming language's surface form is known as its syntax. Most programming languages are purely textual; they use sequences of text including words, numbers, and punctuation, much like written natural languages. On the other hand, there are some programming languages which are more graphical in nature, using visual relationships between symbols to specify a program.
The syntax of a language describes the possible combinations of symbols that form a syntactically correct program. The meaning given to a combination of symbols is handled by semantics (either formal or hard-coded in a reference implementation). Since most languages are textual, this article discusses textual syntax.
Programming language syntax is usually defined using a combination of regular expressions (for lexical structure) and Backus–Naur Form (for grammatical structure).Below is a simple grammar, based on Lisp:
This grammar specifies the following:
an expression is either an atom or a list;
an atom is either a number or a symbol;
a number is an unbroken sequence of one or more decimal digits, optionally preceded by a plus or minus sign;
a symbol is a letter followed by zero or more of any characters (excluding whitespace); and
a list is a matched pair of parentheses, with zero or more expressions inside it.
The following are examples of well-formed token sequences in this grammar: '12345', '()', '(a b c232 (1))'
Not all syntactically correct programs are semantically correct. Many syntactically correct programs are nonetheless ill-formed, per the language's rules; and may (depending on the language specification and the soundness of the implementation) result in an error on translation or execution. In some cases, such programs may exhibit undefined behavior. Even when a program is well-defined within a language, it may still have a meaning that is not intended by the person who wrote it.
Using natural language as an example, it may not be possible to assign a meaning to a grammatically correct sentence or the sentence may be false:
"Colorless green ideas sleep furiously." is grammatically well-formed but has no generally accepted meaning.
"John is a married bachelor." is grammatically well-formed but expresses a meaning that cannot be true.
The following C language fragment is syntactically correct, but performs an operation that is not semantically defined (because p is a null pointer, the operations p->real and p->im have no meaning):
complex *p = NULL;
complex abs_p = sqrt (p->real * p->real + p->im * p->im);
If the type declaration on the first line were omitted, the program would trigger an error on compilation, as the variable "p" would not be defined. But the program would still be syntactically correct, since type declarations provide only semantic information.
The grammar needed to specify a programming language can be classified by its position in the Chomsky hierarchy. The syntax of most programming languages can be specified using a Type-2 grammar, i.e., they are context-free grammars.[25] Some languages, including Perl and Lisp, contain constructs that allow execution during the parsing phase. Languages that have constructs that allow the programmer to alter the behavior of the parser make syntax analysis an undecidable problem, and generally blur the distinction between parsing and execution.[26] In contrast to Lisp's macro system and Perl's BEGIN blocks, which may contain general computations, C macros are merely string replacements, and do not require code execution.[27]
header 1 header 2 header 3
row 1, cell 1 row 1, cell 2 row 1, cell 3
row 2, cell 1 row 2, cell 2 row 2, cell 3
[edit] Static semantics
The static semantics defines restrictions on the structure of valid texts that are hard or impossible to express in standard syntactic formalisms.[1] For compiled languages, static semantics essentially include those semantic rules that can be checked at compile time. Examples include checking that every identifier is declared before it is used (in languages that require such declarations) or that the labels on the arms of a case statement are distinct.[28] Many important restrictions of this type, like checking that identifiers are used in the appropriate context (e.g. not adding a integer to a function name), or that subroutine calls have the appropriate number and type of arguments can be enforced by defining them as rules in a logic called a type system. Other forms of static analyses like data flow analysis may also be part of static semantics. Newer programming languages like Java and C# have definite assignment analysis, a form of data flow analysis, as part of their static semantics.
[edit] Type system
Main articles: Type system and Type safety
A type system defines how a programming language classifies values and expressions into types, how it can manipulate those types and how they interact. The goal of a type system is to verify and usually enforce a certain level of correctness in programs written in that language by detecting certain incorrect operations. Any decidable type system involves a trade-off: while it rejects many incorrect programs, it can also prohibit some correct, albeit unusual programs. In order to bypass this downside, a number of languages have type loopholes, usually unchecked casts that may be used by the programmer to explicitly allow a normally disallowed operation between different types. In most typed languages, the type system is used only to type check programs, but a number of languages, usually functional ones, perform type inference, which relieves the programmer from writing type annotations. The formal design and study of type systems is known as type theory.
[edit] Typed versus untyped languages
A language is typed if the specification of every operation defines types of data to which the operation is applicable, with the implication that it is not applicable to other types.[29] For example, "this text between the quotes" is a string. In most programming languages, dividing a number by a string has no meaning. Most modern programming languages will therefore reject any program attempting to perform such an operation. In some languages, the meaningless operation will be detected when the program is compiled ("static" type checking), and rejected by the compiler, while in others, it will be detected when the program is run ("dynamic" type checking), resulting in a runtime exception.
A special case of typed languages are the single-type languages. These are often scripting or markup languages, such as REXX or SGML, and have only one data type—most commonly character strings which are used for both symbolic and numeric data.
In contrast, an untyped language, such as most assembly languages, allows any operation to be performed on any data, which are generally considered to be sequences of bits of various lengths.[29] High-level languages which are untyped include BCPL and some varieties of Forth.
In practice, while few languages are considered typed from the point of view of type theory (verifying or rejecting all operations), most modern languages offer a degree of typing.[29] Many production languages provide means to bypass or subvert the type system.
[edit] Static versus dynamic typing
In static typing all expressions have their types determined prior to the program being run (typically at compile-time). For example, 1 and (2+2) are integer expressions; they cannot be passed to a function that expects a string, or stored in a variable that is defined to hold dates.[29]
Statically typed languages can be either manifestly typed or type-inferred. In the first case, the programmer must explicitly write types at certain textual positions (for example, at variable declarations). In the second case, the compiler infers the types of expressions and declarations based on context. Most mainstream statically typed languages, such as C++, C# and Java, are manifestly typed. Complete type inference has traditionally been associated with less mainstream languages, such as Haskell and ML. However, many manifestly typed languages support partial type inference; for example, Java and C# both infer types in certain limited cases.[30]
Dynamic typing, also called latent typing, determines the type-safety of operations at runtime; in other words, types are associated with runtime values rather than textual expressions.[29] As with type-inferred languages, dynamically typed languages do not require the programmer to write explicit type annotations on expressions. Among other things, this may permit a single variable to refer to values of different types at different points in the program execution. However, type errors cannot be automatically detected until a piece of code is actually executed, making debugging more difficult. Ruby, Lisp, JavaScript, and Python are dynamically typed.
[edit] Weak and strong typing
Weak typing allows a value of one type to be treated as another, for example treating a string as a number.[29] This can occasionally be useful, but it can also allow some kinds of program faults to go undetected at compile time and even at runtime.
Strong typing prevents the above. An attempt to perform an operation on the wrong type of value raises an error.[29] Strongly typed languages are often termed type-safe or safe.
An alternative definition for "weakly typed" refers to languages, such as Perl and JavaScript, which permit a large number of implicit type conversions. In JavaScript, for example, the expression 2 * x implicitly converts x to a number, and this conversion succeeds even if x is null, undefined, an Array, or a string of letters. Such implicit conversions are often useful, but they can mask programming errors.
Strong and static are now generally considered orthogonal concepts, but usage in the literature differs. Some use the term strongly typed to mean strongly, statically typed, or, even more confusingly, to mean simply statically typed. Thus C has been called both strongly typed and weakly, statically typed.[31][32]
[edit] Execution semantics
Further information: Formal semantics of programming languages
Once data has been specified, the machine must be instructed to perform operations on the data. For example, the semantics may define the strategy by which expressions are evaluated to values, or the manner in which control structures conditionally execute statements. The execution semantics (also known as dynamic semantics) of a language defines how and when the various constructs of a language should produce a program behavior. There are many ways of defining execution semantics. Natural language is often used to specify the execution semantics of languages commonly used in practice. A significant amount of academic research went into formal semantics of programming languages, which allow execution semantics to be specified in a formal manner. Results from this field of research have seen limited application to programming language design and implementation outside academia.
[edit] Core library
Main article: Standard library
Most programming languages have an associated core library (sometimes known as the 'standard library', especially if it is included as part of the published language standard), which is conventionally made available by all implementations of the language. Core libraries typically include definitions for commonly used algorithms, data structures, and mechanisms for input and output.
A language's core library is often treated as part of the language by its users, although the designers may have treated it as a separate entity. Many language specifications define a core that must be made available in all implementations, and in the case of standardized languages this core library may be required. The line between a language and its core library therefore differs from language to language. Indeed, some languages are designed so that the meanings of certain syntactic constructs cannot even be described without referring to the core library. For example, in Java, a string literal is defined as an instance of the java.lang.String class; similarly, in Smalltalk, an anonymous function expression (a "block") constructs an instance of the library's BlockContext class. Conversely, Scheme contains multiple coherent subsets that suffice to construct the rest of the language as library macros, and so the language designers do not even bother to say which portions of the language must be implemented as language constructs, and which must be implemented as parts of a library.
[edit] Design and implementation
Programming languages share properties with natural languages related to their purpose as vehicles for communication, having a syntactic form separate from its semantics, and showing language families of related languages branching one from another.[3] But as artificial constructs, they also differ in fundamental ways from languages that have evolved through usage. A significant difference is that a programming language can be fully described and studied in its entirety, since it has a precise and finite definition.[33] By contrast, natural languages have changing meanings given by their users in different communities. While constructed languages are also artificial languages designed from the ground up with a specific purpose, they lack the precise and complete semantic definition that a programming language has.
Many languages have been designed from scratch, altered to meet new needs, combined with other languages, and eventually fallen into disuse. Although there have been attempts to design one "universal" programming language that serves all purposes, all of them have failed to be generally accepted as filling this role.[34] The need for diverse programming languages arises from the diversity of contexts in which languages are used:
Programs range from tiny scripts written by individual hobbyists to huge systems written by hundreds of programmers.
Programmers range in expertise from novices who need simplicity above all else, to experts who may be comfortable with considerable complexity.
Programs must balance speed, size, and simplicity on systems ranging from microcontrollers to supercomputers.
Programs may be written once and not change for generations, or they may undergo continual modification.
Finally, programmers may simply differ in their tastes: they may be accustomed to discussing problems and expressing them in a particular language.
One common trend in the development of programming languages has been to add more ability to solve problems using a higher level of abstraction. The earliest programming languages were tied very closely to the underlying hardware of the computer. As new programming languages have developed, features have been added that let programmers express ideas that are more remote from simple translation into underlying hardware instructions. Because programmers are less tied to the complexity of the computer, their programs can do more computing with less effort from the programmer. This lets them write more functionality per time unit.[35]
Natural language processors have been proposed as a way to eliminate the need for a specialized language for programming. However, this goal remains distant and its benefits are open to debate. Edsger W. Dijkstra took the position that the use of a formal language is essential to prevent the introduction of meaningless constructs, and dismissed natural language programming as "foolish".[36] Alan Perlis was similarly dismissive of the idea.[37]
A language's designers and users must construct a number of artifacts that govern and enable the practice of programming. The most important of these artifacts are the language specification and implementation.
[edit] Specification
Main article: Programming language specification
The specification of a programming language is intended to provide a definition that the language users and the implementors can use to determine whether the behavior of a program is correct, given its source code.
A programming language specification can take several forms, including the following:
An explicit definition of the syntax, static semantics, and execution semantics of the language. While syntax is commonly specified using a formal grammar, semantic definitions may be written in natural language (e.g., as in the C language), or a formal semantics (e.g., as in Standard ML[38] and Scheme[39] specifications).
A description of the behavior of a translator for the language (e.g., the C++ and Fortran specifications). The syntax and semantics of the language have to be inferred from this description, which may be written in natural or a formal language.
A reference or model implementation, sometimes written in the language being specified (e.g., Prolog or ANSI REXX[40]). The syntax and semantics of the language are explicit in the behavior of the reference implementation.
[edit] Implementation
Main article: Programming language implementation
An implementation of a programming language provides a way to execute that program on one or more configurations of hardware and software. There are, broadly, two approaches to programming language implementation: compilation and interpretation. It is generally possible to implement a language using either technique.
The output of a compiler may be executed by hardware or a program called an interpreter. In some implementations that make use of the interpreter approach there is no distinct boundary between compiling and interpreting. For instance, some implementations of BASIC compile and then execute the source a line at a time.
Programs that are executed directly on the hardware usually run several orders of magnitude faster than those that are interpreted in software.[citation needed]
One technique for improving the performance of interpreted programs is just-in-time compilation. Here the virtual machine, just before execution, translates the blocks of bytecode which are going to be used to machine code, for direct execution on the hardware.
[edit] Usage
Thousands of different programming languages have been created, mainly in the computing field.[41] Programming languages differ from most other forms of human expression in that they require a greater degree of precision and completeness. When using a natural language to communicate with other people, human authors and speakers can be ambiguous and make small errors, and still expect their intent to be understood. However, figuratively speaking, computers "do exactly what they are told to do", and cannot "understand" what code the programmer intended to write. The combination of the language definition, a program, and the program's inputs must fully specify the external behavior that occurs when the program is executed, within the domain of control of that program.
A programming language provides a structured mechanism for defining pieces of data, and the operations or transformations that may be carried out automatically on that data. A programmer uses the abstractions present in the language to represent the concepts involved in a computation. These concepts are represented as a collection of the simplest elements available (called primitives).[42] Programming is the process by which programmers combine these primitives to compose new programs, or adapt existing ones to new uses or a changing environment.
Programs for a computer might be executed in a batch process without human interaction, or a user might type commands in an interactive session of an interpreter. In this case the "commands" are simply programs, whose execution is chained together. When a language is used to give commands to a software application (such as a shell) it is called a scripting language.[citation needed]
[edit] Measuring language usage
Main article: Measuring programming language popularity
It is difficult to determine which programming languages are most widely used, and what usage means varies by context. One language may occupy the greater number of programmer hours, a different one have more lines of code, and a third utilize the most CPU time. Some languages are very popular for particular kinds of applications. For example, COBOL is still strong in the corporate data center, often on large mainframes; FORTRAN in engineering applications; C in embedded applications and operating systems; and other languages are regularly used to write many different kinds of applications.
Various methods of measuring language popularity, each subject to a different bias over what is measured, have been proposed:
counting the number of job advertisements that mention the language[43]
the number of books sold that teach or describe the language[44]
estimates of the number of existing lines of code written in the language—which may underestimate languages not often found in public searches[45]
counts of language references (i.e., to the name of the language) found using a web search engine.
Combining and averaging information from various internet sites, langpop.com claims that [46] in 2008 the 10 most cited programming languages are (in alphabetical order): C, C++, C#, Java, JavaScript, Perl, PHP, Python, Ruby, and SQL.
[edit] Taxonomies
For more details on this topic, see Categorical list of programming languages.
There is no overarching classification scheme for programming languages. A given programming language does not usually have a single ancestor language. Languages commonly arise by combining the elements of several predecessor languages with new ideas in circulation at the time. Ideas that originate in one language will diffuse throughout a family of related languages, and then leap suddenly across familial gaps to appear in an entirely different family.
The task is further complicated by the fact that languages can be classified along multiple axes. For example, Java is both an object-oriented language (because it encourages object-oriented organization) and a concurrent language (because it contains built-in constructs for running multiple threads in parallel). Python is an object-oriented scripting language.
In broad strokes, programming languages divide into programming paradigms and a classification by intended domain of use. Traditionally, programming languages have been regarded as describing computation in terms of imperative sentences, i.e. issuing commands. These are generally called imperative programming languages. A great deal of research in programming languages has been aimed at blurring the distinction between a program as a set of instructions and a program as an assertion about the desired answer, which is the main feature of declarative programming.[47] More refined paradigms include procedural programming, object-oriented programming, functional programming, and logic programming; some languages are hybrids of paradigms or multi-paradigmatic. An assembly language is not so much a paradigm as a direct model of an underlying machine architecture. By purpose, programming languages might be considered general purpose, system programming languages, scripting languages, domain-specific languages, or concurrent/distributed languages (or a combination of these).[48] Some general purpose languages were designed largely with educational goals.[49]
A programming language may also be classified by factors unrelated to programming paradigm. For instance, most programming languages use English language keywords, while a minority do not. Other languages may be classified as being esoteric or not.
History:
Early developments
The first programming languages predate the modern computer. The 19th century had "programmable" looms and player piano scrolls which implemented what are today recognized as examples of domain-specific languages. By the beginning of the twentieth century, punch cards encoded data and directed mechanical processing. In the 1930s and 1940s, the formalisms of Alonzo Church's lambda calculus and Alan Turing's Turing machines provided mathematical abstractions for expressing algorithms; the lambda calculus remains influential in language design.[50]
In the 1940s, the first electrically powered digital computers were created. The first high-level programming language to be designed for a computer was Plankalkül, developed for the German Z3 by Konrad Zuse between 1943 and 1945. However, it was not implemented until 1998 and 2000.[51]
Programmers of early 1950s computers, notably UNIVAC I and IBM 701, used machine language programs, that is, the first generation language (1GL). 1GL programming was quickly superseded by similarly machine-specific, but mnemonic, second generation languages (2GL) known as assembly languages or "assembler". Later in the 1950s, assembly language programming, which had evolved to include the use of macro instructions, was followed by the development of "third generation" programming languages (3GL), such as FORTRAN, LISP, and COBOL.[52] 3GLs are more abstract and are "portable", or at least implemented similarly on computers that do not support the same native machine code. Updated versions of all of these 3GLs are still in general use, and each has strongly influenced the development of later languages.[53] At the end of the 1950s, the language formalized as ALGOL 60 was introduced, and most later programming languages are, in many respects, descendants of Algol.[53] The format and use of the early programming languages was heavily influenced by the constraints of the interface.[54]
[edit] Refinement
The period from the 1960s to the late 1970s brought the development of the major language paradigms now in use, though many aspects were refinements of ideas in the very first Third-generation programming languages:
APL introduced array programming and influenced functional programming.[55]
PL/I (NPL) was designed in the early 1960s to incorporate the best ideas from FORTRAN and COBOL.
In the 1960s, Simula was the first language designed to support object-oriented programming; in the mid-1970s, Smalltalk followed with the first "purely" object-oriented language.
C was developed between 1969 and 1973 as a system programming language, and remains popular.[56]
Prolog, designed in 1972, was the first logic programming language.
In 1978, ML built a polymorphic type system on top of Lisp, pioneering statically typed functional programming languages.
Each of these languages spawned an entire family of descendants, and most modern languages count at least one of them in their ancestry.
The 1960s and 1970s also saw considerable debate over the merits of structured programming, and whether programming languages should be designed to support it.[57] Edsger Dijkstra, in a famous 1968 letter published in the Communications of the ACM, argued that GOTO statements should be eliminated from all "higher level" programming languages.[58]
The 1960s and 1970s also saw expansion of techniques that reduced the footprint of a program as well as improved productivity of the programmer and user. The card deck for an early 4GL was a lot smaller for the same functionality expressed in a 3GL deck.
[edit] Consolidation and growth
The 1980s were years of relative consolidation. C++ combined object-oriented and systems programming. The United States government standardized Ada, a systems programming language derived from Pascal and intended for use by defense contractors. In Japan and elsewhere, vast sums were spent investigating so-called "fifth generation" languages that incorporated logic programming constructs.[59] The functional languages community moved to standardize ML and Lisp. Rather than inventing new paradigms, all of these movements elaborated upon the ideas invented in the previous decade.
One important trend in language design during the 1980s was an increased focus on programming for large-scale systems through the use of modules, or large-scale organizational units of code. Modula-2, Ada, and ML all developed notable module systems in the 1980s, although other languages, such as PL/I, already had extensive support for modular programming. Module systems were often wedded to generic programming constructs.[60]
The rapid growth of the Internet in the mid-1990s created opportunities for new languages. Perl, originally a Unix scripting tool first released in 1987, became common in dynamic websites. Java came to be used for server-side programming. These developments were not fundamentally novel, rather they were refinements to existing languages and paradigms, and largely based on the C family of programming languages.
Programming language evolution continues, in both industry and research. Current directions include security and reliability verification, new kinds of modularity (mixins, delegates, aspects), and database integration such as Microsoft's LINQ.
The 4GLs are examples of languages which are domain-specific, such as SQL, which manipulates and returns sets of data rather than the scalar values which are canonical to most programming languages. Perl, for example, with its 'here document' can hold multiple 4GL programs, as well as multiple JavaScript programs, in part of its own perl code and use variable interpolation in the 'here document' to support multi-language programming.[6
References
^ a b c Aaby, Anthony (2004). Introduction to Programming Languages. http://burks.brighton.ac.uk/burks/pcinfo/progdocs/plbook/index.htm.
^ In mathematical terms, this means the programming language is Turing-complete MacLennan, Bruce J. (1987). Principles of Programming Languages. Oxford University Press. p. 1. ISBN 0-19-511306-3.
^ a b Steven R. Fischer, A history of language, Reaktion Books, 2003, ISBN 186189080X, p. 205
^ ACM SIGPLAN (2003). "Bylaws of the Special Interest Group on Programming Languages of the Association for Computing Machinery". http://www.acm.org/sigs/sigplan/sigplan_bylaws.htm. Retrieved 2006-06-19. , The scope of SIGPLAN is the theory, design, implementation, description, and application of computer programming languages - languages that permit the specification of a variety of different computations, thereby providing the user with significant control (immediate or delayed) over the computer's operation.
^ Dean, Tom (2002). "Programming Robots". Building Intelligent Robots. Brown University Department of Computer Science. http://www.cs.brown.edu/people/tld/courses/cs148/02/programming.html. Retrieved 2006-09-23.
^ R. Narasimahan, Programming Languages and Computers: A Unified Metatheory, pp. 189--247 in Franz Alt, Morris Rubinoff (eds.) Advances in computers, Volume 8, Academic Press, 1994, ISBN 012012108, p.193 : "a complete specification of a programming language must, by definition, include a specification of a processor--idealized, if you will--for that language." [the source cites many references to support this statement]
^ Ben Ari, Mordechai (1996). Understanding Programming Languages". John Wiley and Sons. "Programs and languages can be defined as purely formal mathematical objects. However, more people are interested in programs than in other mathematical objects such as groups, precisely because it is possible to use the program—the sequence of symbols—to control the execution of a computer. While we highly recommend the study of the theory of programming, this text will generally limit itself to the study of programs as they are executed on a computer."
^ David A. Schmidt, The structure of typed programming languages, MIT Press, 1994, ISBN 0262193493, p. 32
^ Pierce, Benjamin (2002). Types and Programming Languages. MIT Press. p. 339. ISBN 0-262-16209-1.
^ Digital Equipment Corporation. "Information Technology - Database Language SQL (Proposed revised text of DIS 9075)". ISO/IEC 9075:1992, Database Language SQL. http://www.contrib.andrew.cmu.edu/~shadow/sql/sql1992.txt. Retrieved June 29, 2006.
^ The Charity Development Group (December 1996). "The CHARITY Home Page". http://pll.cpsc.ucalgary.ca/charity1/www/home.html. Retrieved 2006-06-29. , Charity is a categorical programming language..., All Charity computations terminate.
^ XML in 10 points W3C, 1999, XML is not a programming language.
^ Powell, Thomas (2003). HTML & XHTML: the complete reference. McGraw-Hill. p. 25. ISBN 0-07-222-942-X. "HTML is not a programming language."
^ Dykes, Lucinda (2005). XML For Dummies, 4th Edition. Wiley. p. 20. ISBN 0-7645-8845-1. "...it's a markup language, not a programming language."
^ http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/library/x-xslt/
^ http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms767587(VS.85).aspx
^ Scott, Michael (2006). Programming Language Pragmatics. Morgan Kaufmann. p. 802. ISBN 0-12-633951-1. "XSLT, though highly specialized to the transformation of XML, is a Turing-complete programming language."
^ http://tobi.oetiker.ch/lshort/lshort.pdf
^ Syropoulos, Apostolos; Antonis Tsolomitis, Nick Sofroniou (2003). Digital typography using LaTeX. Springer-Verlag. p. 213. ISBN 0-387-95217-9. "TeX is not only an excellent typesetting engine but also a real programming language."
^ Robert A. Edmunds, The Prentice-Hall standard glossary of computer terminology, Prentice-Hall, 1985, p. 91
^ Pascal Lando, Anne Lapujade, Gilles Kassel, and Frédéric Fürst, Towards a General Ontology of Computer Programs, ICSOFT 2007, pp. 163-170
^ S.K. Bajpai, Introduction To Computers And C Programming, New Age International, 2007, ISBN 812241379X, p. 346
^ R. Narasimahan, Programming Languages and Computers: A Unified Metatheory, pp. 189--247 in Franz Alt, Morris Rubinoff (eds.) Advances in computers, Volume 8, Academic Press, 1994, ISBN 012012108, p.215: "[...] the model [...] for computer languages differs from that [...] for programming languages in only two respects. In a computer language, there are only finitely many names--or registers--which can assume only finitely many values--or states--and these states are not further distinguished in terms of any other attributes. [author's footnote:] This may sound like a truism but its implications are far reaching. For example, it would imply that any model for programming languages, by fixing certain of its parameters or features, should be reducible in a natural way to a model for computer languages."
^ John C. Reynolds, Some thoughts on teaching programming and programming languages, SIGPLAN Notices, Volume 43, Issue 11, November 2008, p.109
^ Michael Sipser (1997). Introduction to the Theory of Computation. PWS Publishing. ISBN 0-534-94728-X. Section 2.2: Pushdown Automata, pp.101–114.
^ Jeffrey Kegler, "Perl and Undecidability", The Perl Review. Papers 2 and 3 prove, using respectively Rice's theorem and direct reduction to the halting problem, that the parsing of Perl programs is in general undecidable.
^ Marty Hall, 1995, Lecture Notes: Macros, PostScript version
^ Michael Lee Scott, Programming language pragmatics, Edition 2, Morgan Kaufmann, 2006, ISBN 0126339511, p. 18-19
^ a b c d e f g Andrew Cooke. "An Introduction to Programming Languages". http://www.acooke.org/andrew/writing/lang.html#sec-types. Retrieved June 30, 2006. [dead link]
^ Specifically, instantiations of generic types are inferred for certain expression forms. Type inference in Generic Java—the research language that provided the basis for Java 1.5's bounded parametric polymorphism extensions—is discussed in two informal manuscripts from the Types mailing list: Generic Java type inference is unsound (Alan Jeffrey, 17 December 2001) and Sound Generic Java type inference (Martin Odersky, 15 January 2002). C#'s type system is similar to Java's, and uses a similar partial type inference scheme.
^ "Revised Report on the Algorithmic Language Scheme (February 20, 1998)". http://www.schemers.org/Documents/Standards/R5RS/HTML/r5rs-Z-H-4.html. Retrieved June 9, 2006.
^ Luca Cardelli and Peter Wegner. "On Understanding Types, Data Abstraction, and Polymorphism". Manuscript (1985). http://citeseer.ist.psu.edu/cardelli85understanding.html. Retrieved June 9, 2006.
^ Jing Huang. "Artificial Language vs. Natural Language". http://www.cs.cornell.edu/info/Projects/Nuprl/cs611/fall94notes/cn2/subsection3_1_3.html.
^ IBM in first publishing PL/I, for example, rather ambitiously titled its manual The universal programming language PL/I (IBM Library; 1966). The title reflected IBM's goals for unlimited subsetting capability: PL/I is designed in such a way that one can isolate subsets from it satisfying the requirements of particular applications. ("Encyclopaedia of Mathematics » P » PL/I". SpringerLink. http://eom.springer.de/P/p072885.htm. Retrieved June 29, 2006. ). Ada and UNCOL had similar early goals.
^ Frederick P. Brooks, Jr.: The Mythical Man-Month, Addison-Wesley, 1982, pp. 93-94
^ Dijkstra, Edsger W. On the foolishness of "natural language programming." EWD667.
^ Perlis, Alan, Epigrams on Programming. SIGPLAN Notices Vol. 17, No. 9, September 1982, pp. 7-13
^ Milner, R.; M. Tofte, R. Harper and D. MacQueen. (1997). The Definition of Standard ML (Revised). MIT Press. ISBN 0-262-63181-4.
^ Kelsey, Richard; William Clinger and Jonathan Rees (February 1998). "Section 7.2 Formal semantics". Revised5 Report on the Algorithmic Language Scheme. http://www.schemers.org/Documents/Standards/R5RS/HTML/r5rs-Z-H-10.html#%_sec_7.2. Retrieved 2006-06-09.
^ ANSI — Programming Language Rexx, X3-274.1996
^ "HOPL: an interactive Roster of Programming Languages". Australia: Murdoch University. http://hopl.murdoch.edu.au/. Retrieved 2009-06-01. "This site lists 8512 languages."
^ Abelson, Sussman, and Sussman. "Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs". http://mitpress.mit.edu/sicp/full-text/book/book-Z-H-10.html. Retrieved 2009-03-03.
^ Survey of Job advertisements mentioning a given language
^ Counting programming languages by book sales
^ Bieman, J.M.; Murdock, V., Finding code on the World Wide Web: a preliminary investigation, Proceedings First IEEE International Workshop on Source Code Analysis and Manipulation, 2001
^ Programming Language Popularity
^ Carl A. Gunter, Semantics of Programming Languages: Structures and Techniques, MIT Press, 1992, ISBN 0262570955, p. 1
^ "TUNES: Programming Languages". http://tunes.org/wiki/programming_20languages.html.
^ Wirth, Niklaus (1993). "Recollections about the development of Pascal". Proc. 2nd ACM SIGPLAN conference on history of programming languages: 333–342. doi:10.1145/154766.155378. http://portal.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=155378. Retrieved 2006-06-30.
^ Benjamin C. Pierce writes:
"... the lambda calculus has seen widespread use in the specification of programming language features, in language design and implementation, and in the study of type systems."
Pierce, Benjamin C. (2002). Types and Programming Languages. MIT Press. p. 52. ISBN 0-262-16209-1.
^ Rojas, Raúl, et al. (2000). "Plankalkül: The First High-Level Programming Language and its Implementation". Institut für Informatik, Freie Universität Berlin, Technical Report B-3/2000. (full text)
^ Linda Null, Julia Lobur, The essentials of computer organization and architecture, Edition 2, Jones & Bartlett Publishers, 2006, ISBN 0763737690, p. 435
^ a b O'Reilly Media. "History of programming languages" (PDF). http://www.oreilly.com/news/graphics/prog_lang_poster.pdf. Retrieved October 5, 2006.
^ Frank da Cruz. IBM Punch Cards Columbia University Computing History.
^ Richard L. Wexelblat: History of Programming Languages, Academic Press, 1981, chapter XIV.
^ François Labelle. "Programming Language Usage Graph". SourceForge. http://www.cs.berkeley.edu/~flab/languages.html. Retrieved June 21, 2006. . This comparison analyzes trends in number of projects hosted by a popular community programming repository. During most years of the comparison, C leads by a considerable margin; in 2006, Java overtakes C, but the combination of C/C++ still leads considerably.
^ Hayes, Brian (2006), "The Semicolon Wars", American Scientist 94 (4): 299–303
^ Dijkstra, Edsger W. (March 1968). "Go To Statement Considered Harmful". Communications of the ACM 11 (3): 147–148. doi:10.1145/362929.362947. http://www.acm.org/classics/oct95/. Retrieved 2006-06-29.
^ Tetsuro Fujise, Takashi Chikayama Kazuaki Rokusawa, Akihiko Nakase (December 1994). "KLIC: A Portable Implementation of KL1" Proc. of FGCS '94, ICOT Tokyo, December 1994. KLIC is a portable implementation of a concurrent logic programming language KL1.
^ Jim Bender (March 15, 2004). "Mini-Bibliography on Modules for Functional Programming Languages". ReadScheme.org. http://readscheme.org/modules/. Retrieved 2006-09-27.
^ Wall, Programming Perl ISBN 0-596-00027-8 p.66
This article is about IP addresses in general. For the Wikipedia user access level, see Wikipedia:User access levels#Anonymous users.
An Internet Protocol (IP) address is a numerical label that is assigned to devices participating in a computer network, that uses the Internet Protocol for communication between its nodes.[1] An IP address serves two principal functions: host or network interface identification and location addressing. Its role has been characterized as follows: "A name indicates what we seek. An address indicates where it is. A route indicates how to get there."[2]
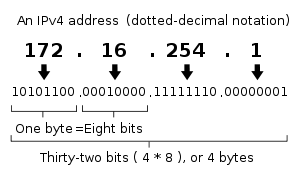
The designers of TCP/IP defined an IP address as a 32-bit number[1] and this system, known as Internet Protocol Version 4 or IPv4, is still in use today. However, due to the enormous growth of the Internet and the resulting depletion of available addresses, a new addressing system (IPv6), using 128 bits for the address, was developed in 1995[3] and last standardized by RFC 2460 in 1998.[4] Although IP addresses are stored as binary numbers, they are usually displayed in human-readable notations, such as 208.77.188.166 (for IPv4), and 2001:db8:0:1234:0:567:1:1 (for IPv6).
The Internet Protocol also routes data packets between networks; IP addresses specify the locations of the source and destination nodes in the topology of the routing system. For this purpose, some of the bits in an IP address are used to designate a subnetwork. The number of these bits is indicated in CIDR notation, appended to the IP address; e.g., 208.77.188.166/24.
As the development of private networks raised the threat of IPv4 address exhaustion, RFC 1918 set aside a group of private address spaces that may be used by anyone on private networks. They are often used with network address translators to connect to the global public Internet.
The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA), which manages the IP address space allocations globally, cooperates with five Regional Internet Registries (RIRs) to allocate IP address blocks to Local Internet Registries (Internet service providers) and other entities.
IP versions
Two versions of the Internet Protocol (IP) are in use: IP Version 4 and IP Version 6
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)